继续
0x00.前言
0x01.引用 1.0 TensorFlow实现线性回归模型代码 1.1 前期准备 TensorFlow相关API可以到在实验TensorFlow - 相关 API中学习。
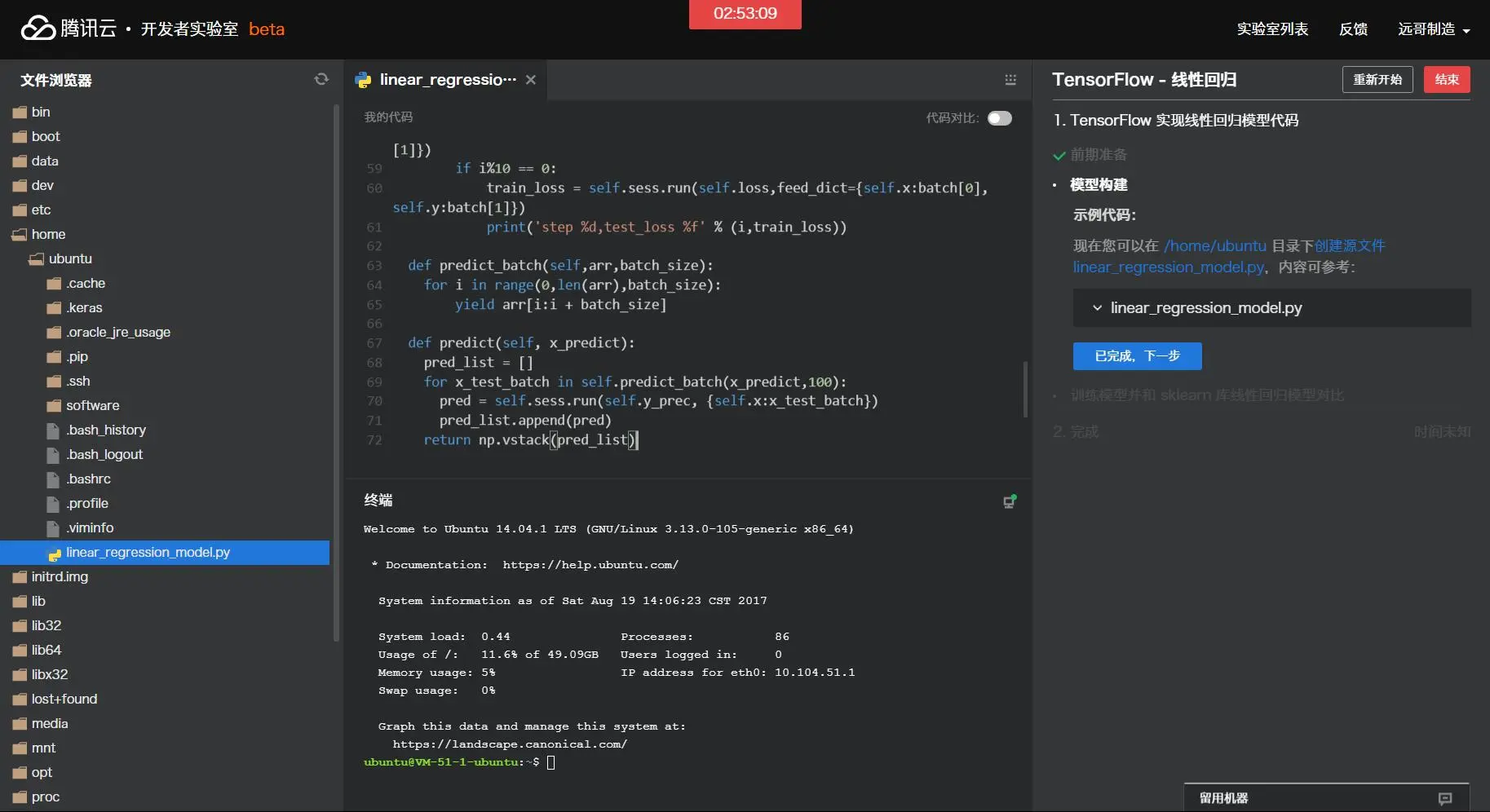
1.2 模型构建 现在您可以在/home/ubuntu目录下创建源文件linear_regression_model.py,内容可参考:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npclass linearRegressionModel : def __init__ (self,x_dimen ): self.x_dimen = x_dimen self._index_in_epoch = 0 self.constructModel() self.sess = tf.Session() self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) def weight_variable (self,shape ): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev = 0.1 ) return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable (self,shape ): initial = tf.constant(0.1 ,shape = shape) return tf.Variable(initial) def next_batch (self,batch_size ): start = self._index_in_epoch self._index_in_epoch += batch_size if self._index_in_epoch > self._num_datas: perm = np.arange(self._num_datas) np.random.shuffle(perm) self._datas = self._datas[perm] self._labels = self._labels[perm] start = 0 self._index_in_epoch = batch_size assert batch_size <= self._num_datas end = self._index_in_epoch return self._datas[start:end],self._labels[start:end] def constructModel (self ): self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None ,self.x_dimen]) self.y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None ,1 ]) self.w = self.weight_variable([self.x_dimen,1 ]) self.b = self.bias_variable([1 ]) self.y_prec = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.x, self.w), self.b) mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.y_prec, self.y)) l2 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.w)) self.loss = mse + 0.15 *l2 self.train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.1 ).minimize(self.loss) def train (self,x_train,y_train,x_test,y_test ): self._datas = x_train self._labels = y_train self._num_datas = x_train.shape[0 ] for i in range (5000 ): batch = self.next_batch(100 ) self.sess.run(self.train_step,feed_dict={self.x:batch[0 ],self.y:batch[1 ]}) if i%10 == 0 : train_loss = self.sess.run(self.loss,feed_dict={self.x:batch[0 ],self.y:batch[1 ]}) print ('step %d,test_loss %f' % (i,train_loss)) def predict_batch (self,arr,batch_size ): for i in range (0 ,len (arr),batch_size): yield arr[i:i + batch_size] def predict (self, x_predict ): pred_list = [] for x_test_batch in self.predict_batch(x_predict,100 ): pred = self.sess.run(self.y_prec, {self.x:x_test_batch}) pred_list.append(pred) return np.vstack(pred_list)
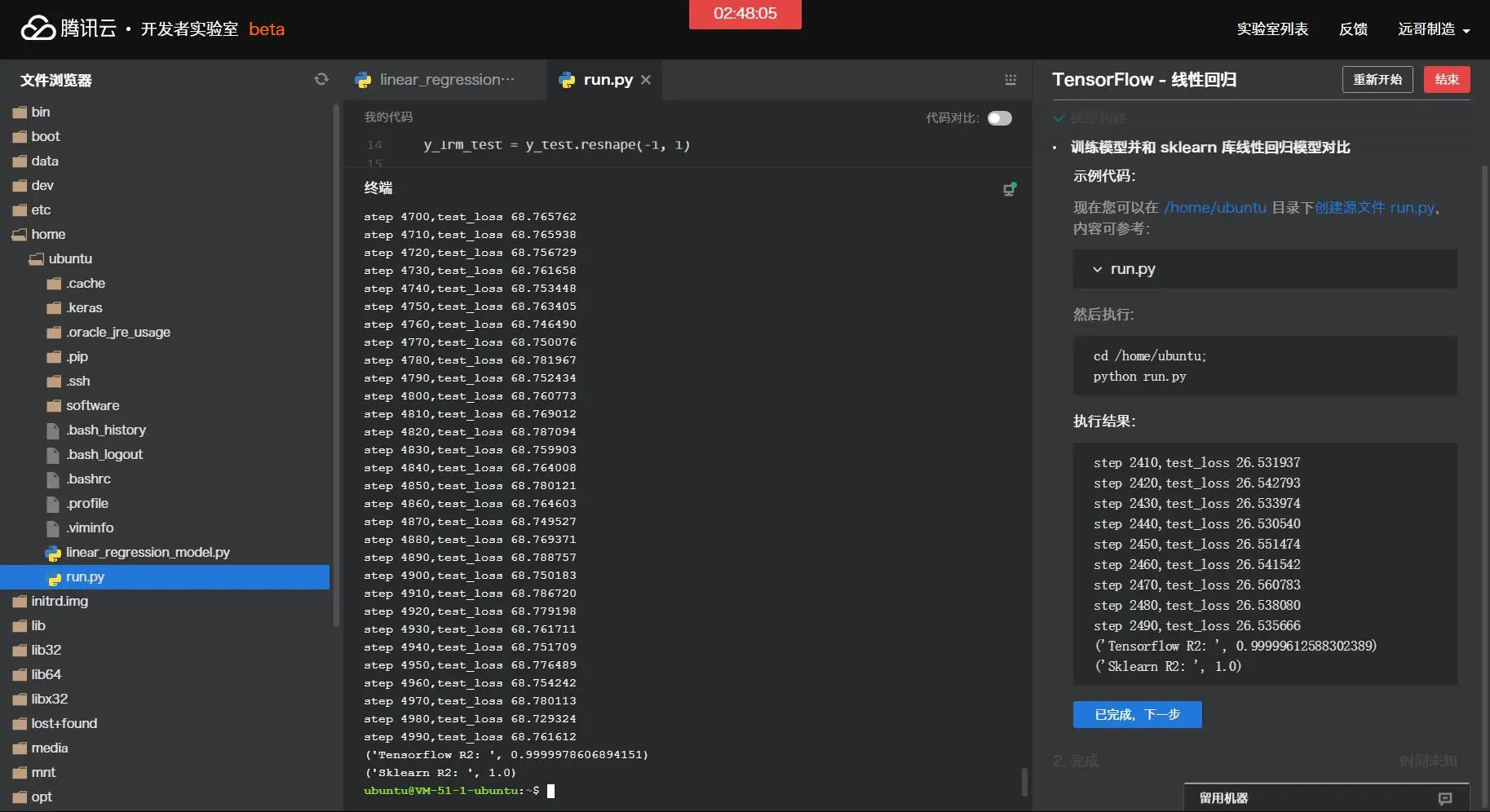
1.3 训练模型并和sklearn库线性回归模型对比 现在您可以在/home/ubuntu目录下创建源文件run.py,内容可参考:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_scorefrom sklearn.datasets import make_regressionfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom linear_regression_model import linearRegressionModel as lrmif __name__ == '__main__' : x, y = make_regression(7000 ) x_train,x_test,y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.5 ) y_lrm_train = y_train.reshape(-1 , 1 ) y_lrm_test = y_test.reshape(-1 , 1 ) linear = lrm(x.shape[1 ]) linear.train(x_train, y_lrm_train,x_test,y_lrm_test) y_predict = linear.predict(x_test) print ("Tensorflow R2: " , r2_score(y_predict.ravel(), y_lrm_test.ravel())) lr = LinearRegression() y_predict = lr.fit(x_train, y_train).predict(x_test) print ("Sklearn R2: " , r2_score(y_predict, y_test))
然后执行:cd /home/ubuntupython run.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 step 2410,test_loss 26.531937 step 2420,test_loss 26.542793 step 2430,test_loss 26.533974 step 2440,test_loss 26.530540 step 2450,test_loss 26.551474 step 2460,test_loss 26.541542 step 2470,test_loss 26.560783 step 2480,test_loss 26.538080 step 2490,test_loss 26.535666 ('Tensorflow R2: ', 0.99999612588302389) ('Sklearn R2: ', 1.0)
0x02.后记 emmm……真的好快
未完待续……